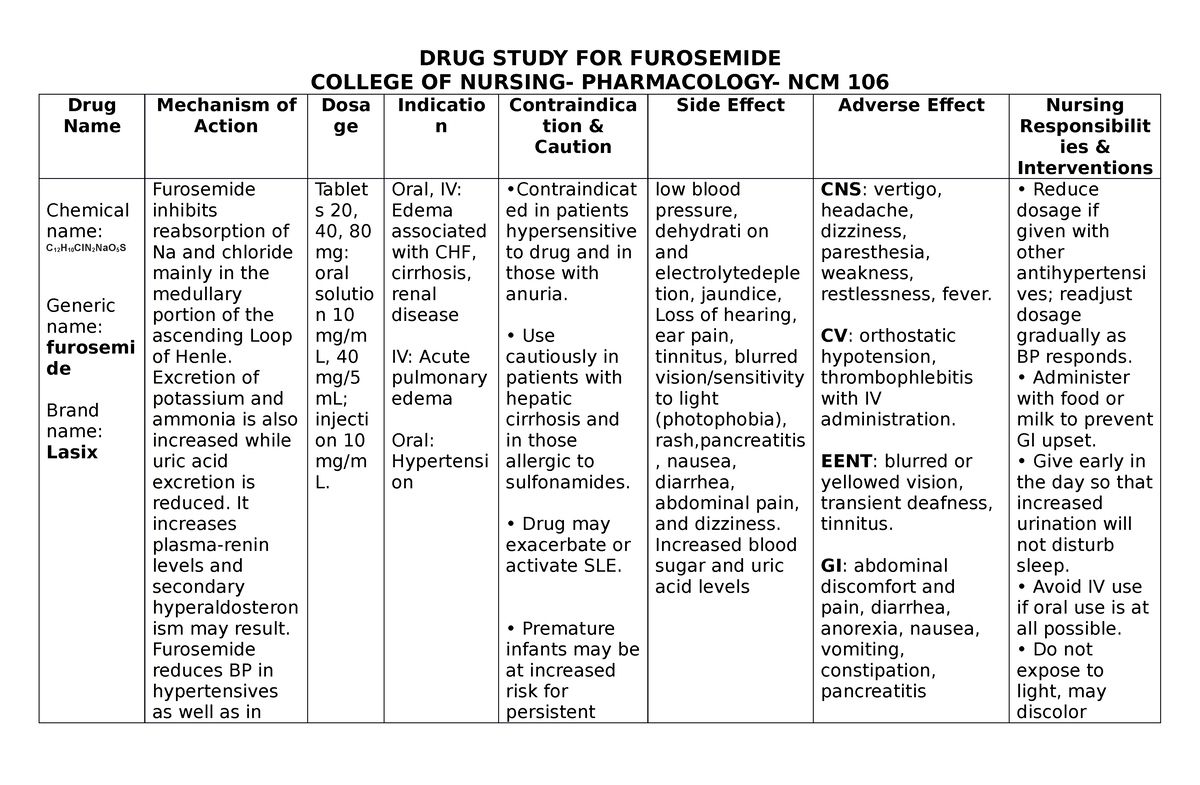
Drug Study of Furosemide DRUG STUDY FOR FUROSEMIDE COLLEGE OF NURSING
furosemide Nursing Considerations & Management - RNpedia Pharmacology & Drug Study (Notes) furosemide Nursing Considerations & Management : furosemide Apo-Furosemide (CAN), Furosemide Special (CAN), Lasix Loop diuretic Pregnancy Category C Dosage & Route :Tablets—20, 40, 80 mg; oral solution—10 mg/mL, 40 mg/5 mL; injection—10 mg/mL
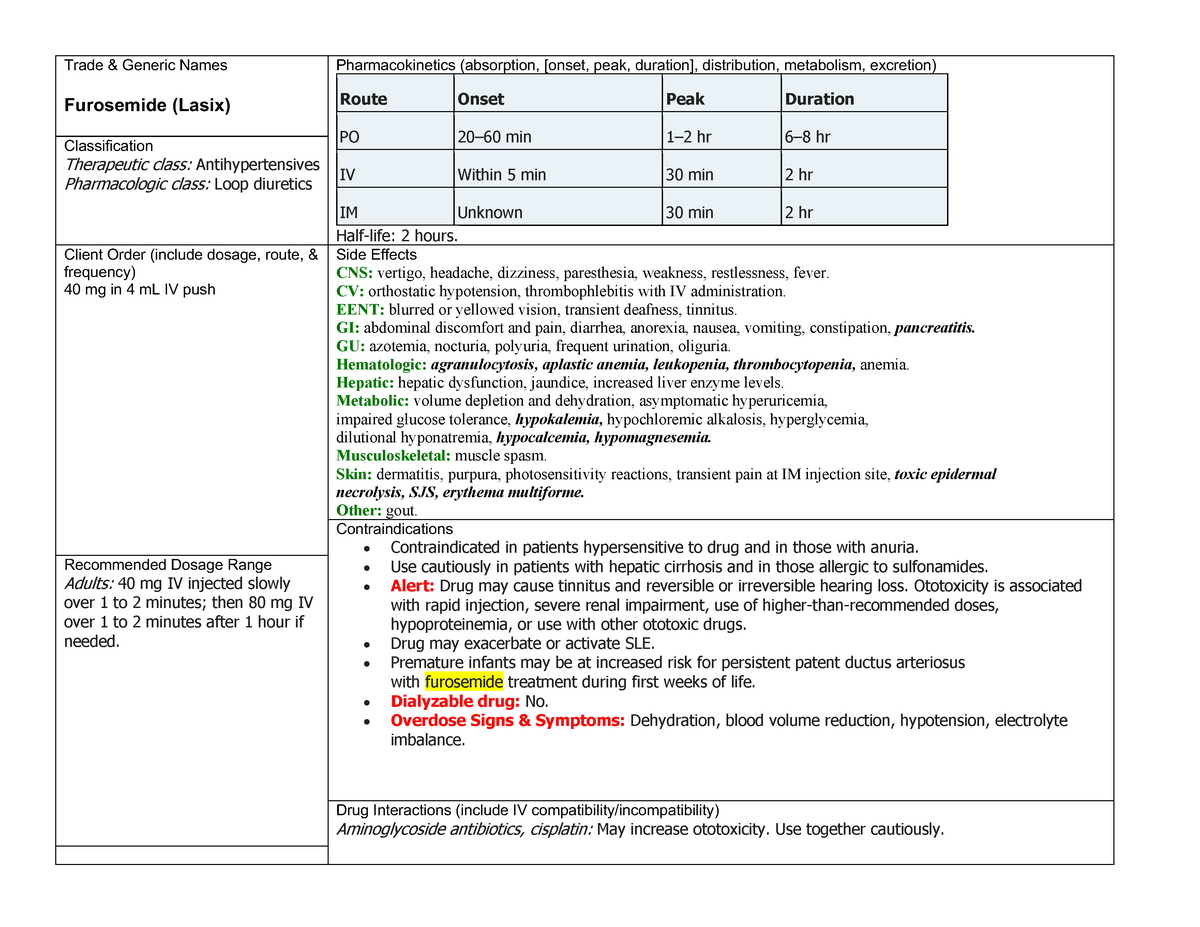
Med Card Furosimide Med Card for Nursing Care Plan Furosemide
Furosemide is used when a stronger diuretic is needed but dose should not be more than 6 mg/kg/d.. These are vital nursing interventions done in patients who are taking diuretics: Administer drug with food or milk if GI upset is a problem to buffer drug effect on the stomach lining.

Furosemide Nursing Considerations
Pronunciation: fur- oh -se-mide Trade Name (s) Furoscix Lasix Ther. Class. diuretics Pharm. Class. loop diuretics Indications PO IM IV Edema due to HF, hepatic impairment, or renal disease. SUBQ Edema due to New York Heart Association class II-III chronic HF. PO Hypertension. Action

Furosemide Nursing Considerations, Side Effects, and Mechanism of
IV furosemide is used to urgently treat pulmonary edema. Nursing Considerations Across the Lifespan. The onset of diuresis following oral administration is within 1 hour. The peak effect occurs within the first or second hour. The duration of diuretic effect is 6 to 8 hours. When possible, loop diuretics should be administered in the morning.

PPT Diuretics and furosmide PowerPoint Presentation, free download
blurred vision, dizziness, headache, vertigo. hearing loss, tinnitus. anorexia, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth, dyspepsia, nausea, pancreatitis, vomiting. photosensitivity, pruritus, rash. hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia. , hypocalcemia, APLASTIC ANEMIA, AGRANULOCYTOSIS, hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. fever, increased BUN, nephr.

Med sheet Lasix furosimide ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES THERAPEUTIC
Furosemide is a loop diuretic that has been in use for decades. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved furosemide to treat conditions with volume overload and edema secondary to congestive heart failure exacerbation, liver failure, or renal failure, including the nephrotic syndrome.
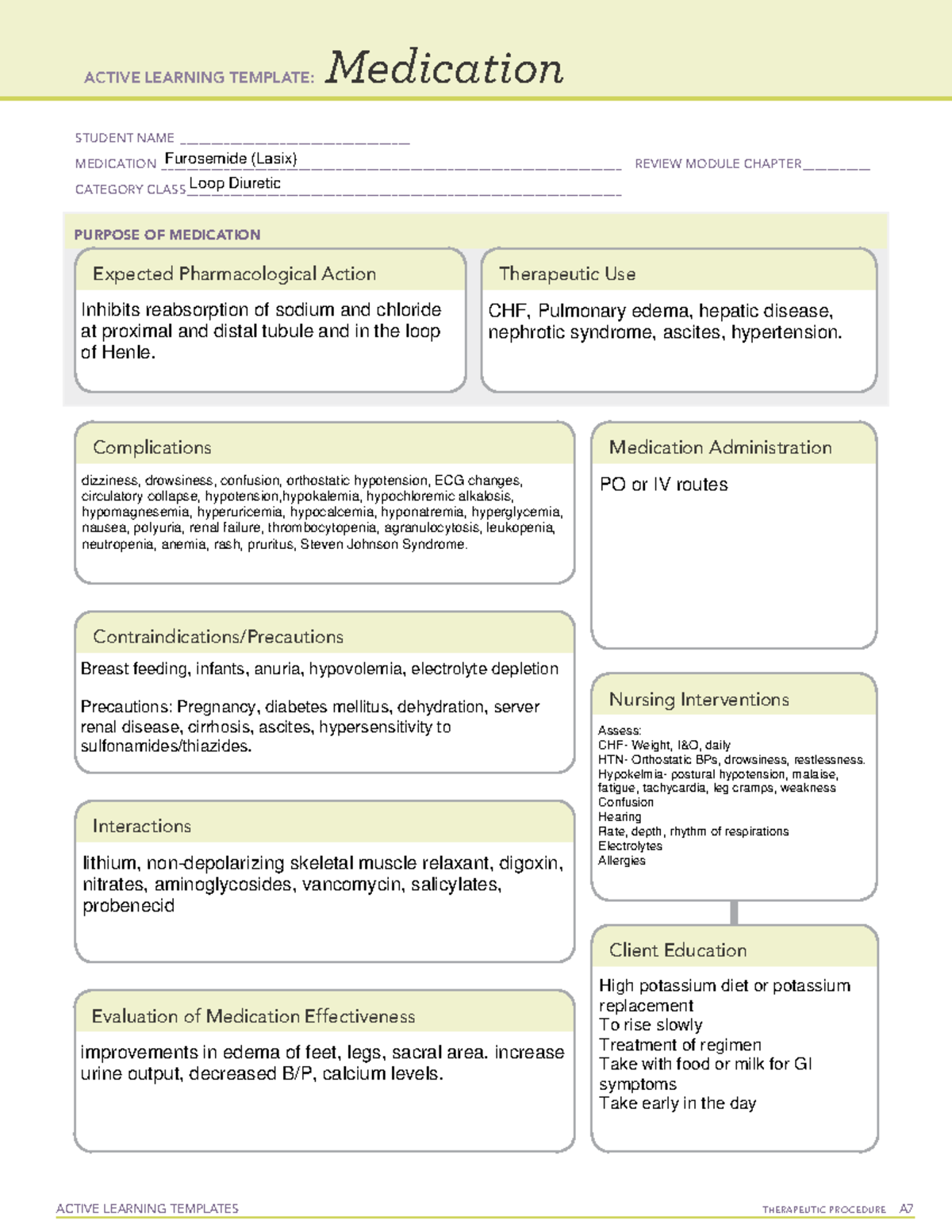
Furosemide Drug Cards ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES THERAPEUTIC
GENERIC AND PROPRIETARY NAMES - Furosemide. - Lasix. ACTION - Inhibits reabsorption from the ascending loop of Henle in the renal tubule. CLASSIFICATION -

FUROSEMIDE MECHANISM OF ACTION (NURSING PHARMACOLOGY) YouTube
Furosemide Nursing Considerations July 6, 2022 by Anna Curran. RN, BSN, PHN Last updated on August 23rd, 2022 at 10:56 am Furosemide Lasix Nursing Implications Furosemide Nursing Pharmacology Furosemide (Lasix) is a prescription drug that belongs to the loop diuretics class and works on the kidneys to remove extra fluid in the body.

Furosemide (Lasix) Nursing Drug Card (Simplified) Pharmacology YouTube
Furosemide Nursing Considerations, Side Effects, and Mechanism of Action Pharmacology for Nurses NURSINGcom w/Jon Haws, RN 252K subscribers Subscribe 565 67K views 6 years ago Nursing.

Furosemide Mechanism of Action (Nursing Pharmacology) (2) Nursing
Furosemide is used to treat clients with edema, and clients with hypertension. IV furosemide is used to urgently treat pulmonary edema. Nursing Considerations Across the Lifespan. The onset of diuresis following oral administration is within 1 hour. The peak effect occurs within the first or second hour. The duration of diuretic effect is 6 to.

Furosemide (Lasix) Drug Study Nursing Journal
Nurses should continually monitor for dehydration and electrolyte imbalances that can occur with excessive diuresis, such as dryness of mouth, thirst, weakness, lethargy, drowsiness, restlessness, muscle pains or cramps, muscular fatigue, hypotension, oliguria, tachycardia, arrhythmia, or gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea and vomiting.

Guidelines for the Use of Furosemide (Lasix )
Nursing Considerations • Use caution with liver disease • May cause hypotension, dry mouth, excessive urination, dehydration, electrolyte abnormalities, metabolic alkalosis • Hypokalemia may lead to increase risk of digoxin toxicity • Monitor renal panel
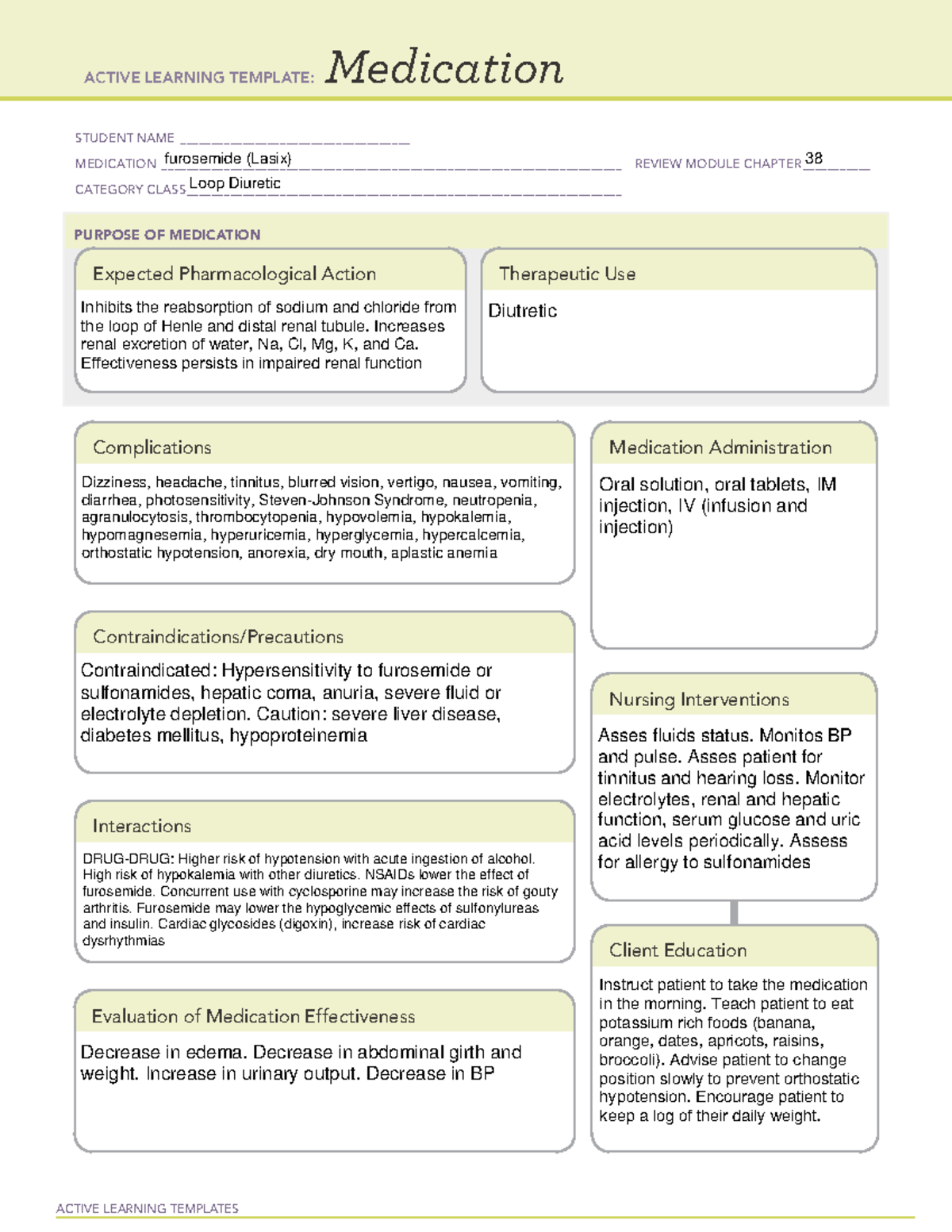
NURS 180 Week 6 Med cards furosemide ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES
Understanding Furosemide Nursing Considerations Furosemide is a commonly used diuretic medication in the field of nursing. As a healthcare professional, it is important to have a thorough understanding of the basics of furosemide and the nursing considerations that come with its use.

Furosemide Mechanism of Action (Nursing Pharmacology) (1) Nursing
This article destinations to provide nurses with an introduction to furosemide, inclusive its pharmacological properties, typical, nursing considerations, potential side impacts, and more.
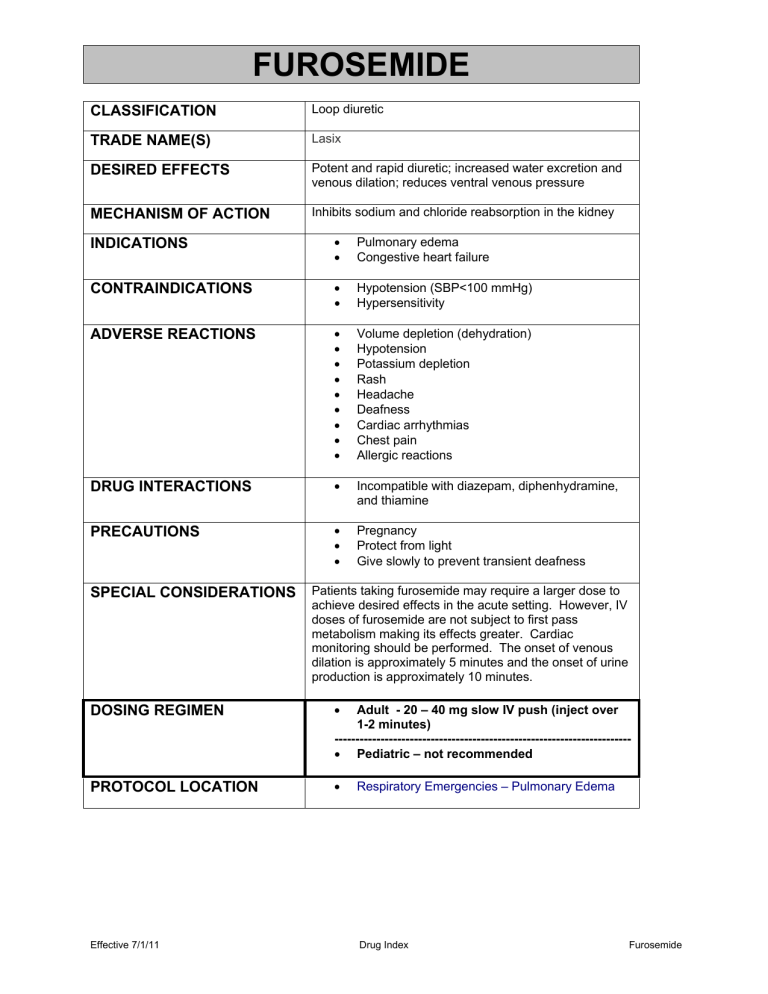
Furosemide Summa Center for EMS
Nursing Considerations for Diuretic Drugs. Here are important nursing considerations when administering this drug: Nursing Assessment.. Furosemide was the first loop diuretic to be approved in the United States (1966) and is still widely used today.

Furosemide 4 Nursing Pediatrics Nursing Pediatrics COMS 2320 TTU
Indications: Furosemide is used to treat client s with edema and is also used to treat hypertension. IV furosemide is used to urgently treat pulmonary edema in conditions such as congestive heart failure. Nursing Considerations: The onset of diuresis following oral administration is within 1 hour. The peak effect occurs within the first or.