
Schematic representation of the electron transfer mechanism in a... Download Scientific Diagram
The diagrams show two ways of representing this electron transfer. Figure caption, The outer electron from a sodium atom transfers to the outer shell of a chlorine atom
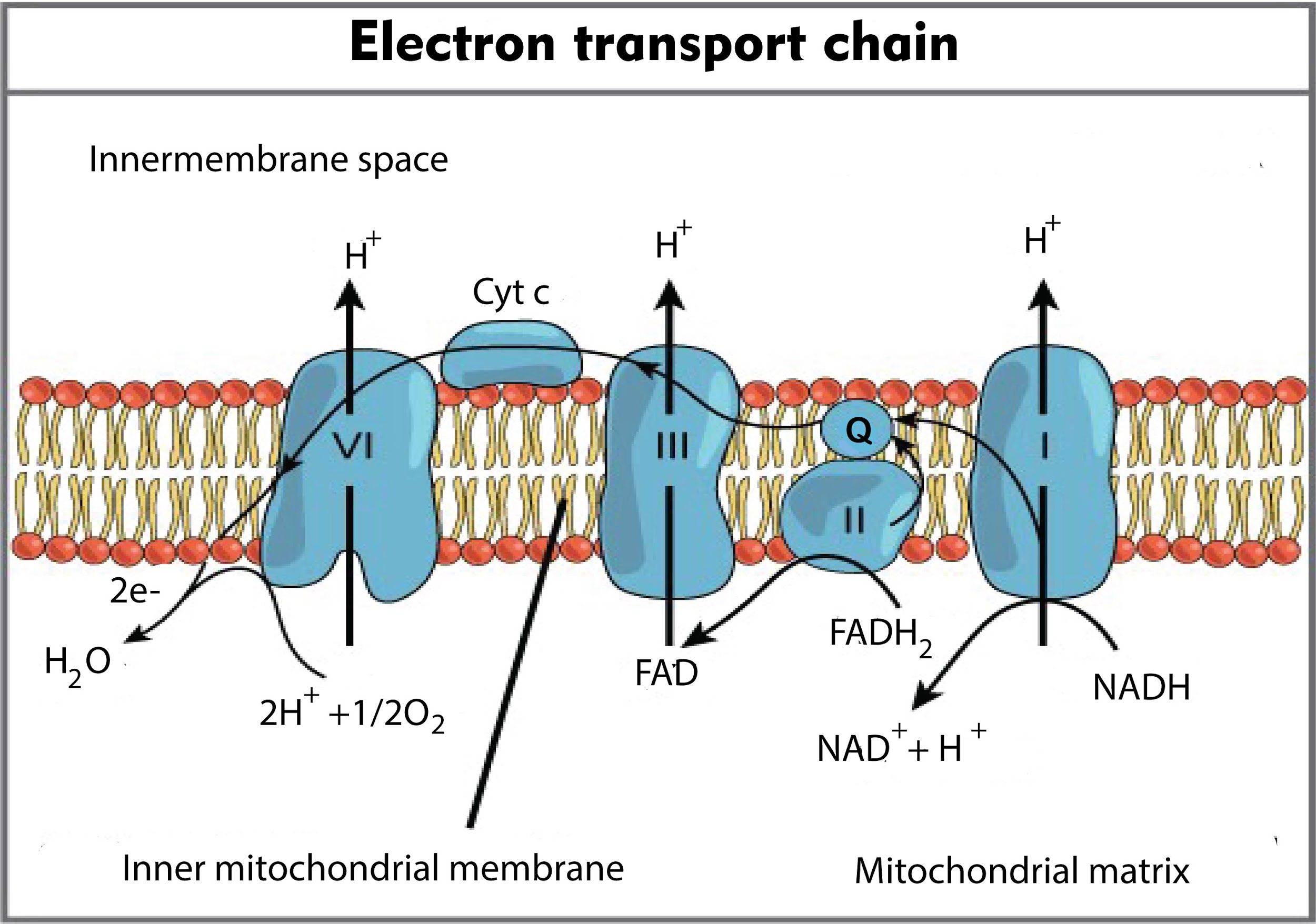
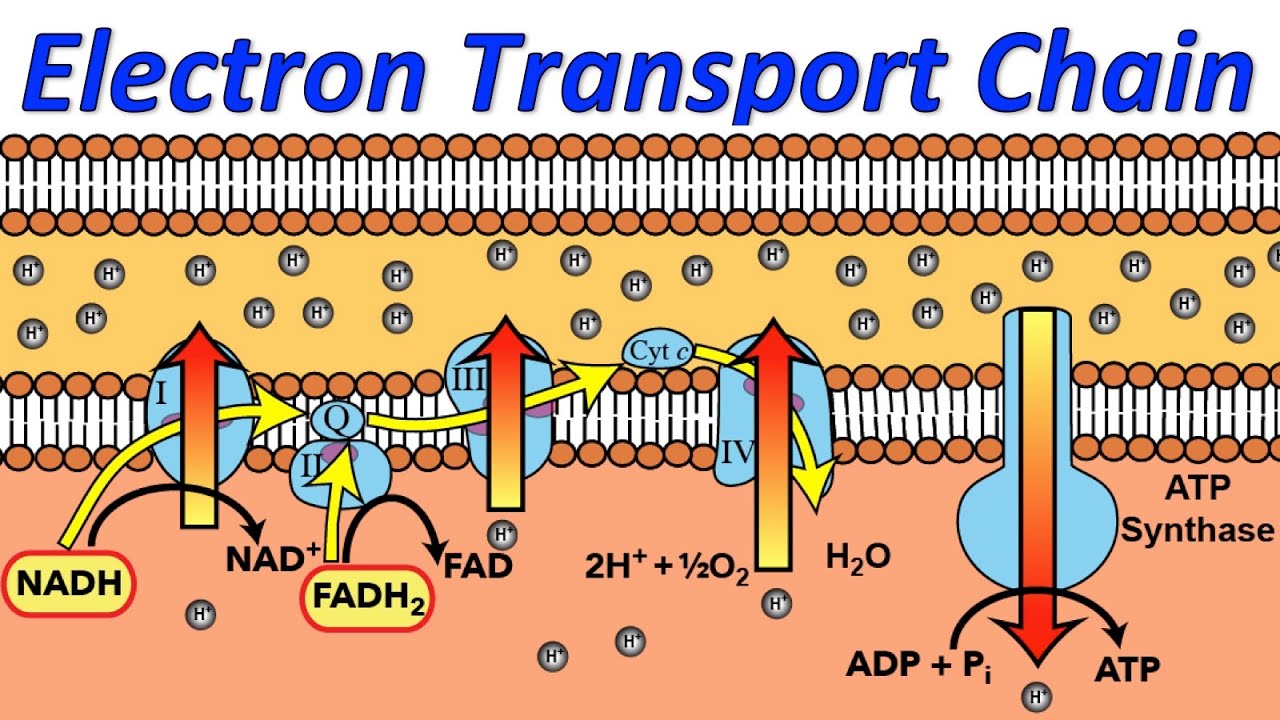
In the electron transport chain during terminal oxidation, the cytochrome, which donates
A. Lewis electron dot diagram. (or electron dot diagram or a Lewis diagram or a Lewis structure) is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the.
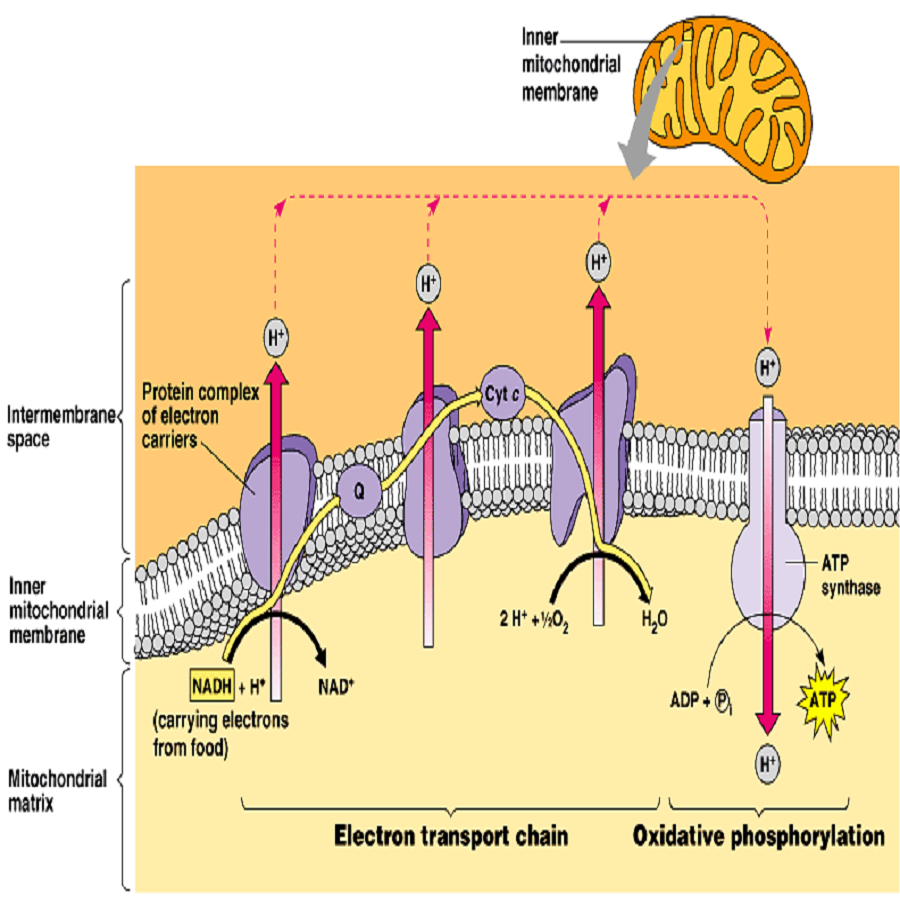
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION, ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN — Biology Notes
Electron transfer reaction. Electron transfer reaction is a reaction in which a single electron is transferred from one molecule to another [1]. For example, a reaction that occurs when steel wool (made of iron atoms) is placed in a solution of CuSO4 is given in Figure 1.25.1 1.25. 1 below: Figure 1.25.1 1.25. 1: An electron transfer reaction [2]
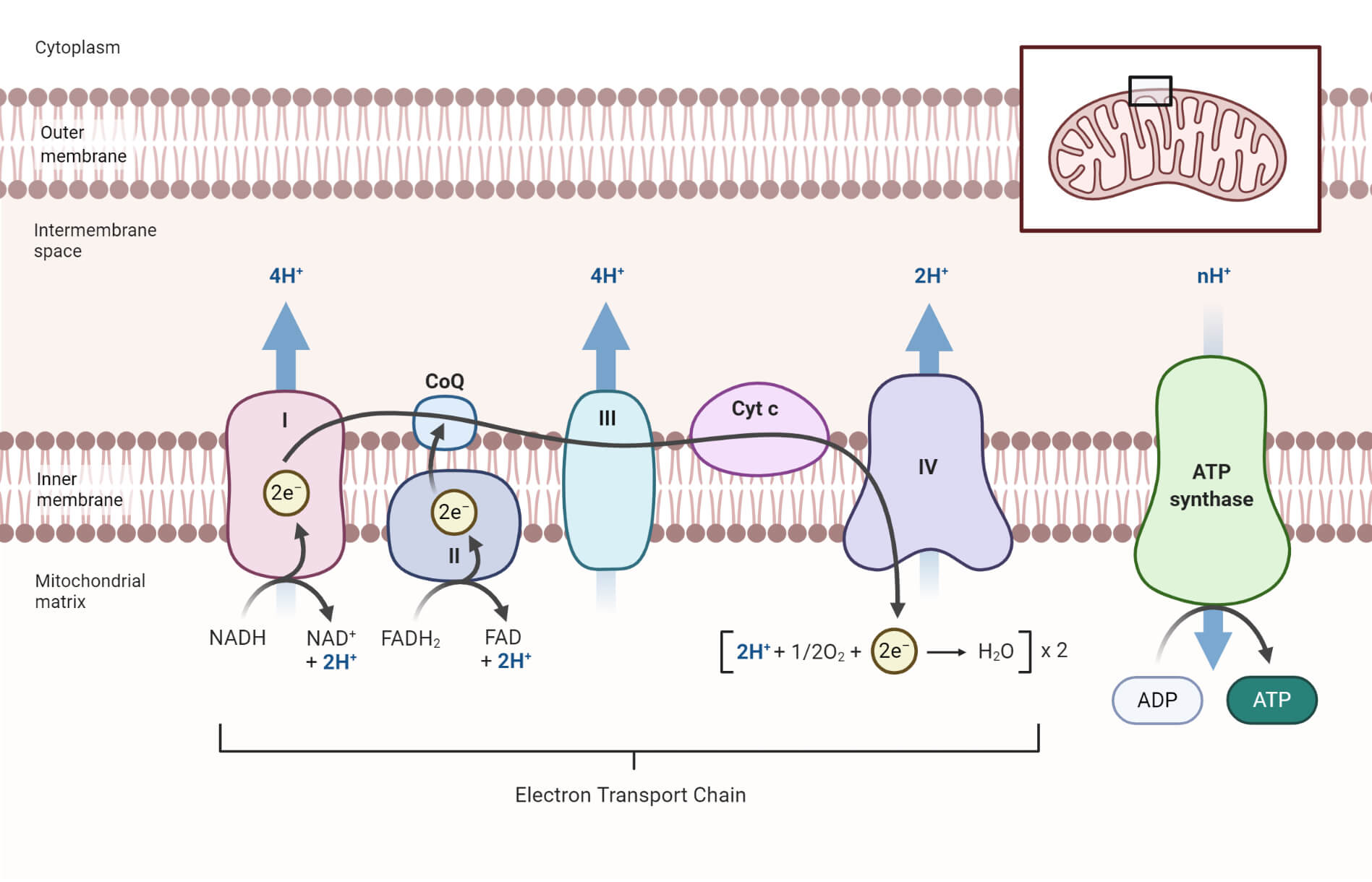
Electron Transport Chain Definition, Components, Steps
Electron Transfer. We can use electron configurations to illustrate the electron transfer process between sodium atoms and chlorine atoms. Recall the electron configuration of sodium from Chapter 2 "Elements, Atoms, and the Periodic Table":. Na: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1. As demonstrated in Example 1 (in Section 3.1 "Two Types of Bonding"), sodium is likely to achieve an octet in its.

Electron Transport Biology Diagram
The attraction of oppositely charged ions caused by electron transfer is called an ionic bond. The strength of ionic bonding depends on the magnitude of the charges and the sizes of the ions. 10.3: Lewis Structures of Ionic Compounds- Electrons Transferred is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by.

Electron Transport Chain — Summary & Diagrams Expii
Answer a. Answer b. Answer c. Exercise 1.10.6 1.10. 6. Outer sphere electron transfer rates depend on the free energy change of the reaction (ΔG°) and the distance between oxidant and reductant (d) according to the relation. Rate constant = k = Ae(−ΔG)e−d k = A e ( − Δ G) e − d. a) What happens to the rate of the reaction as.
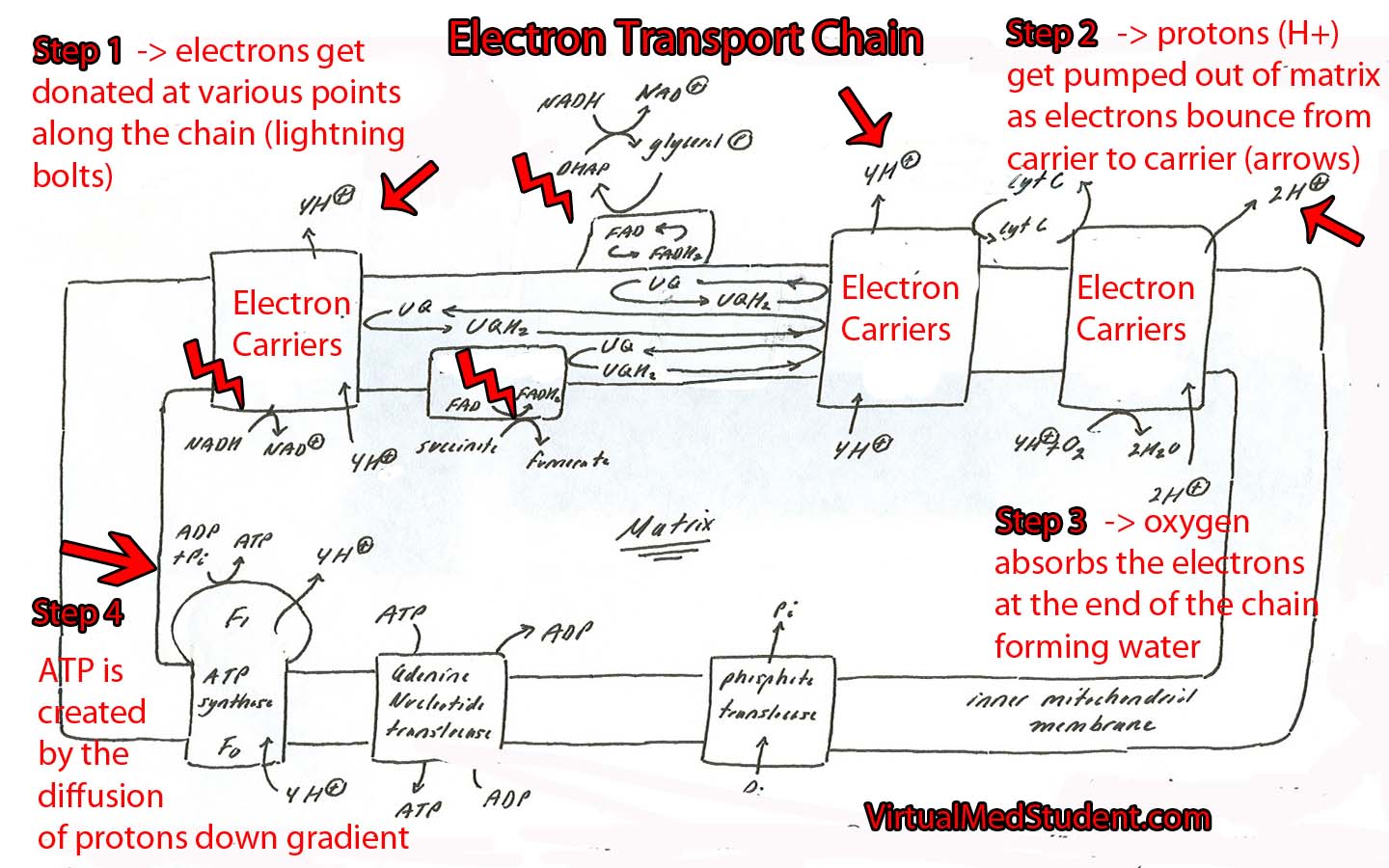
Electron Transport Chain
An electron transfers from the Na atom to the Cl atom: resulting in two ions—the Na + ion and the Cl − ion: Both species now have complete octets, and the electron shells are energetically stable. From basic physics, we know that opposite charges attract. This is what happens to the Na + and Cl − ions:
.svg/1280px-Mitochondrial_electron_transport_chain_(annotated_diagram).svg.png)
FileMitochondrial electron transport chain (annotated diagram).svg Wikipedia
Electron transfer ( ET) occurs when an electron relocates from an atom or molecule to another such chemical entity. ET is a mechanistic description of certain kinds of redox reactions involving transfer of electrons. [2] Electrochemical processes are ET reactions.

Electron Transport Chain Definition, Steps and Diagram (2023)
The attraction between oppositely charged ions is called an ionic bond, and it is one of the main types of chemical bonds in chemistry. Ionic bonds are caused by electrons transferring from one atom to another. In electron transfer, the number of electrons lost must equal the number of electrons gained. We saw this in the formation of NaCl.
Electron Transport Chain Introduction , Steps & Examples
The use of chemically modified proteins to study the distance depen-dence of electron transfer, notably by Gray and coworkers, has opened a whole new field of activity. The interaction of theory and experiment in these many electron transfer fields has been particularly extensive and exciting, and each has stimulated. Rudolph A. Marcus.

Electron Transport Chain — Summary & Diagrams Expii
The rates of electron transfer between cobalt complexes of the bidentate bipyridyl ligand, Co(bipy) 3 n+, are strongly dependent upon oxidation state in the redox pair. Electron transfer between Co(I)/Co(II) occurs with a rate constant of about 10 9 M-1 s-1, whereas the reaction between Co(II)/Co(III) species proceeds with k = 18 M-1 s-1.

Simple Electron Transport Chain
4Al + 3O 2 → 2Al 2 O 3 With oxidation numbers inserted as superscripts, this reaction is written to show that both elements change oxidation numbers. Because the oxidation numbers changed, an oxidation‐reduction reaction is defined as one in which electrons are transferred between atoms.

Biology 141 Electron Transport Chain in Cellular Respiration Diagram Quizlet
A Lewis diagram shows how the valence electrons are distributed around the atoms in a molecule. Shared pairs of electrons are drawn as lines between atoms, while lone pairs of electrons are drawn as dots next to atoms. When constructing a Lewis diagram, keep in mind the octet rule, which refers to the tendency of atoms to gain, lose, or share.
Electron Transport; Respiratory Chain
An electron transfers from the Na atom to the Cl atom: Resulting in two ions — the Na + ion and the Cl − ion: Both species now have complete octets, and the electron shells are energetically stable. From basic physics, we know that opposite charges attract. This is what happens to the Na + and Cl − ions:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/electron_transport-3f9e19fb18564f1ab2ec8ed37954a59c.jpg)
Electron Transport Chain and Energy Production
Electron transfer theory describes the parameters which control the rate at which an electron is transferred from one atom or molecule to another.. Potential energy diagrams for electron transfer reactions. In each of the three examples, the parabolas on the left and right represent the reactant and product states, respectively. In these.

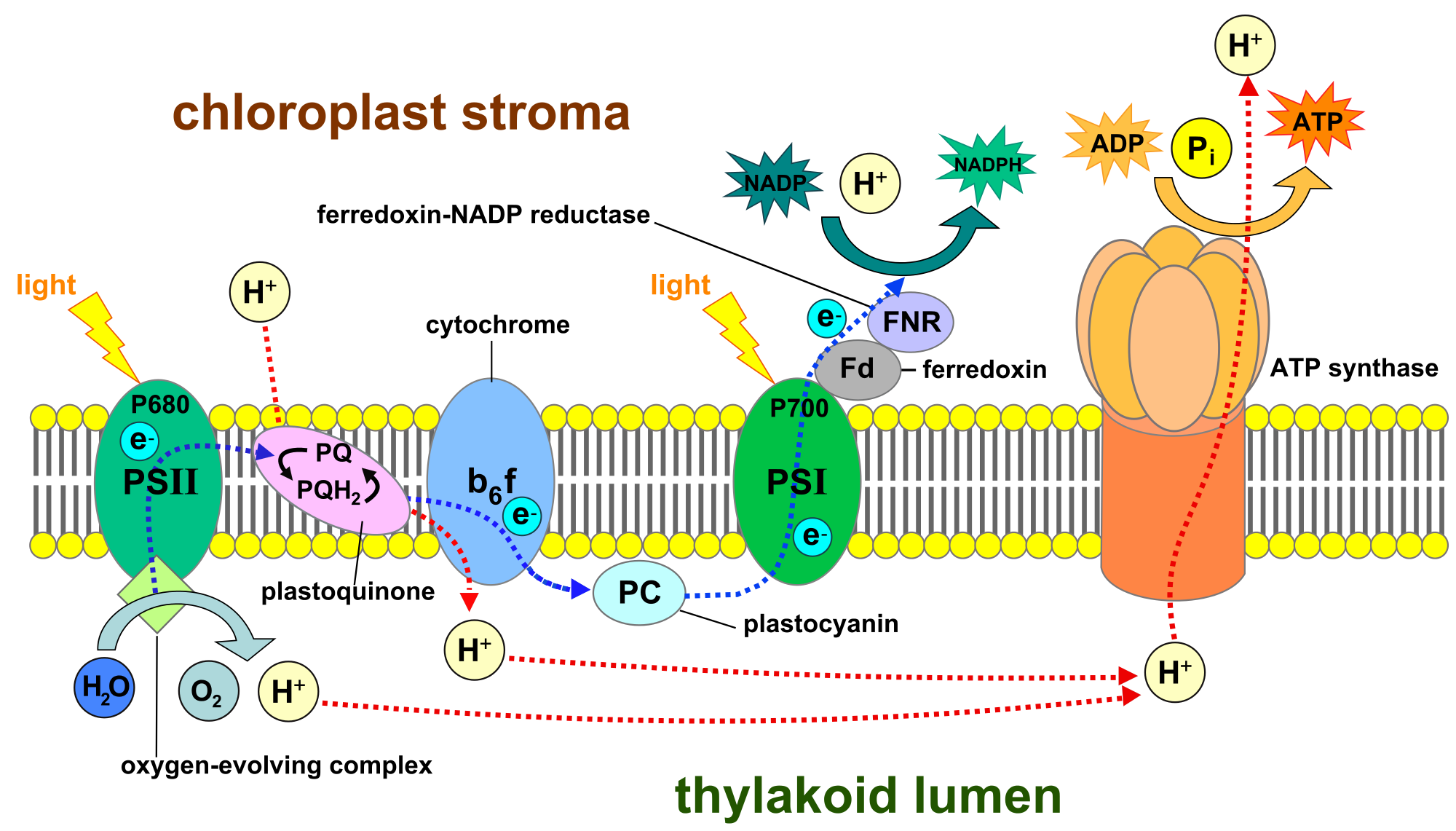
Electron Transport Chain Steps Explained with Diagram Electron transport chain, Light reaction
An electron transfers from the Na atom to the Cl atom: Resulting in two ions — the Na + ion and the Cl − ion: Both species now have complete octets, and the electron shells are energetically stable. From basic physics, we know that opposite charges attract. This is what happens to the Na + and Cl − ions: